Office Address
S.C Chatterjee Road - Bandel
Prantik Benepukir
IN - West Bengal
Hooghly - 712123
The AMD Ryzen 8000G “Hawk Point” Desktop APUs, including the flagship Ryzen 7 8700G, have had their specifications leaked and confirmed by ASUS
Source: WCCF Tech

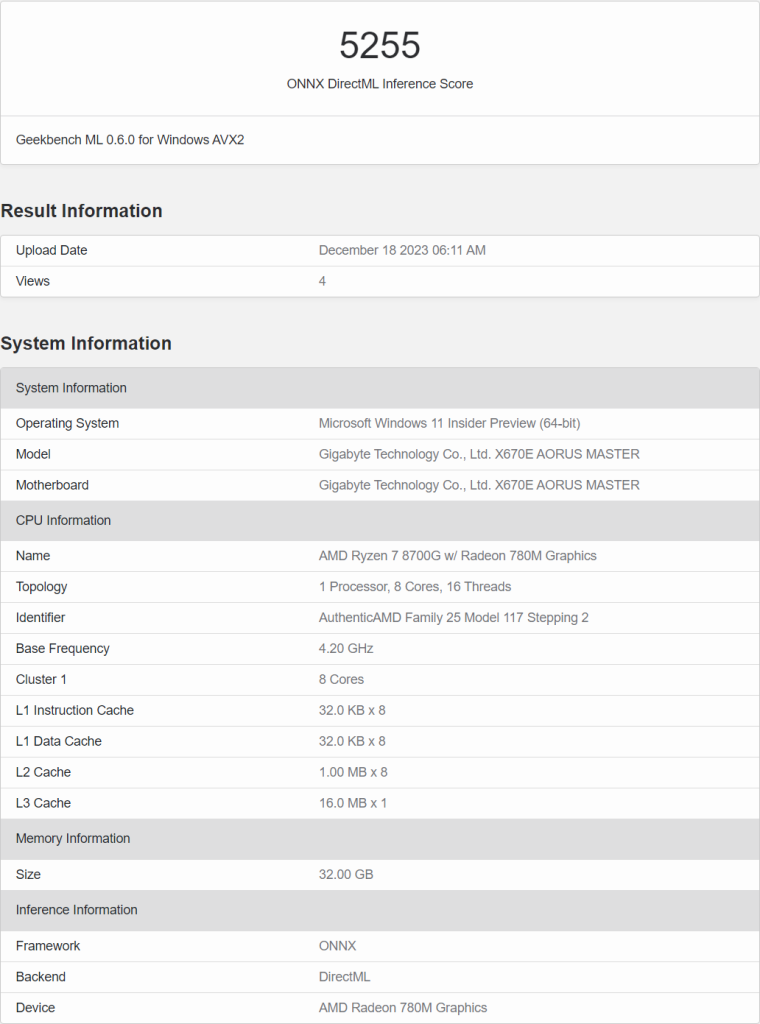
The Ryzen 7 8700G is expected to offer 8 cores, 16 threads, a base clock of 4.2 GHz, and a boost clock of 5.1 GHz. It will also feature a Radeon 780M integrated GPU.
The new Hawk Point APUs in the AM5 Desktop segment will utilize two key technologies: the Zen 4 core architecture, which will power the CPU side, and the RDNA 3 core architecture, which will power the graphics.
The AMD Ryzen 8000G APUs are based on the B2 stepping of Phoenix architecture. The B2 stepping is used by Hawk Point APUs, which have already debuted with AMD’s new Ryzen 8040 APUs for laptops.
The AMD Ryzen 8000G “Hawk Point” Desktop APUs will be available in both 65W and 35W variants. The lineup is led by the Ryzen 7 8700G, a direct successor to the Ryzen 7 5700G “Cezanne.” This chip gets the full 8-core/16-thread “Zen 4” CPU, along with its 16 MB shared L3 cache; and the full-featured Radeon 780M iGPU with its 12 (CU) compute units, worth 768 stream processors.

The AMD Ryzen 8000G APUs will be available in both PRO and Non-PRO flavors, which share identical specifications. The lineup also includes the Ryzen 5 8600G APU, which features 6 cores, 12 threads, a base clock of 4.35 GHz, and a boost clock of 5.0 GHz.
Following the Ryzen 7 8700G is the Ryzen 5 8600G, which is based on the same “Phoenix” silicon as the 8700G, but with 6 out of 8 “Zen 4” cores enabled, and a maximum CPU boost frequency of 4.35 GHz. The 16 MB L3 cache is left untouched, and the Radeon 780M is likely unchanged from the 8700G.
The Ryzen 5 8500G is rumored to be based on the smaller “Phoenix 2” silicon, and to operate at a base clock of 3.55 GHz and a boost clock of 5.0 GHz, while at the entry-level is the Ryzen 3 8300G. This is a quad-core chip based on “Phoenix 2,” in that two out of four “Zen 4c” cores are disabled, leaving it with two “Zen 4” cores, and two “Zen 4c” cores the 8300G operates at a base clock of 3.45 GHz and a boost clock of 4.90 GHz. These two chips feature Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) support but lack manual overclocking capabilities.
It’s also worth noting that the Phoenix 2 chips will not feature higher-end RDNA 3 iGPUs such as the Radeon 780M and 760M. These would instead feature the Radeon 740M with just 4 compute units. It will be interesting to see if AMD adds an NPU to its AM5 Desktop APUs So far, the XDNA Engine has only been limited to Ryzen 7040/8040 laptop chips.
The Phoenix 2 chips also don’t get an NPU due to size/cost limitations but higher-end chips such as the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G may include the NPU, making them the first desktop processors to feature an AI-specific accelerator engine.